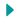
Stem
Stems are the aboveground structures that bear the plant’s leaves and flowers. The stem provides a host of services to the plant:
- It provides a pathway for transporting water up to the leaves, and moving the sugars produced in the leaves down to nourish the roots.
- It acts as a sturdy mast to hold up the leaves and help orient them for maximum exposure to sunlight.
- It can act as a storage site for carbohydrates.
- All stems have nodes along their length. A node is the point at which a leaf attaches to the stem
- The axillary buds are located at the nodes. (Remember that these buds, located just above where the leaf meets the stem, sprout to form new leaves or side shoots.)
- The section of the stem located between two nodes is called the internode.
- The very tip of the stem where the most rapid growth usually occurs is called the apical bud.
Types of stem
Herbaceous
Many familiar garden plants’ stems are soft and green; these are called herbaceous stems.
Their leaves and stems die down to soil level at the end of every growing season. Herbaceous plants can be annual, biennial or perennial.
Examples of herbaceous biennials include carrot , parsnip ; herbaceous perennials include peony, mint and most ferns and most grasses.
Woody
Woody plants are plants with very strong and not easily bendable stems such as trees. They are hard and not very flexible. The stems branches and roots are usually covered with a layer of bark. The wood that woody plants produce allows them to survive harsh winters and continue growing instead of dying.
Examples : Trees and shrubs