A quick look at the Grade 1 lessons :
Weather and The Sky:GK questions on space
Weather and The Sky: Earth and Sky fundamentals
Solar system
Sun :
- It is a star.
- It gives us heat and light
- It is the main source of energy on the earth
- Eight planets and many heavenly bodies revolve around the sun.
Planets :
- Orbits the sun
- Has sufficient mass to be round, or nearly round
- Is not a satellite (moon) of another object
- Has removed debris and small objects from the area around its orbit
- Mercury is the smallest planet and jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system
- Mars is also called the red planet
- The ring of saturn is the most extensive and the ring particles are made almost entirely of water ice, with a trace component of rocky material.
Our Solar system has 8 planets : Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Earth :
- It is the third planet from the sun.
- It is the only planet with life because it had air and water.
- The layer of air surrounding the earth is called the atmosphere
- Earth is also called the blue planet because about three fourths of it’s surface is covered by water
- Different features of the earth’s surface are called landforms
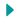
Landforms and waterbodies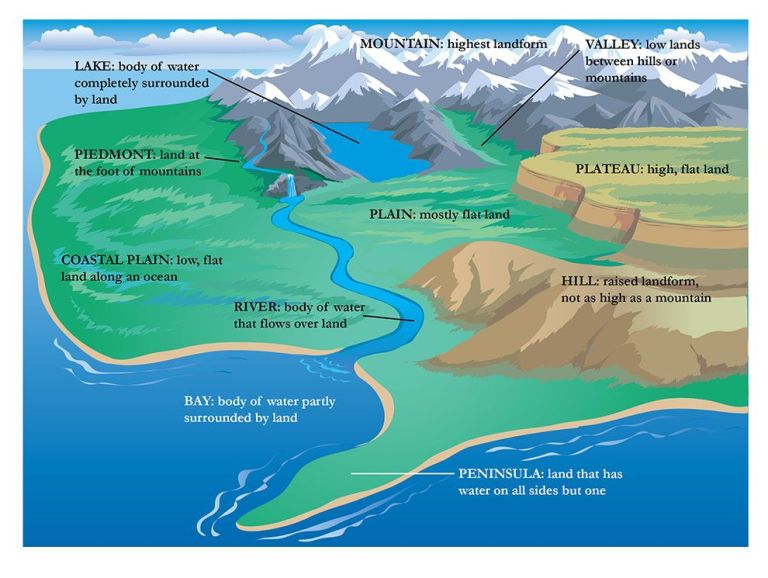
Hills : Raised rocky areas.
Plains : Flat land areas. People live on plains and grow crops and raise animals
Mountains : High landforms which are mostly in the form of peaks. They may be covered in snow and when the snow melts , it changes into water and flow in the form of river or stream
Valleys : Lowland area between two mountains or hills
Island : Land surrounded on all sides by water
Deserts : Dry hot areas of land which receive very less rainfall. They are covered in sand.
Sun and shadow
Transparent
Transparent materials let light pass through them in straight lines, so that you can see clearly through them. Glass is an example of a transparent material.
Translucent
Translucent materials let some light through, but they scatter the light in all directions, so that you cannot see clearly through them. Tissue paper is an example of a translucent material.
Opaque
Opaque materials do not let any light pass through them. They block the light. Wood is an example of an opaque material.
Shadow
A shadow is made when an object blocks light. The shadow appears on the side of the object furthest from the light source.The object must be Opaque or Translucent to make a shadow. A transparent object will not make any shadow, as light will pass straight through it.
Opaque objects make dark shadows. Translucent objects make faint shadows.
- If an object is moved closer to the light source, the shadow gets bigger.
- If an object is moved further away from the light source, the shadow gets smaller.
Shadows made by the Sun
The Sun is a very bright natural light source and moves from east to west.
This movement across the sky directly affects shadows in two ways: size and direction. Shadows are opposite the light source, so when the sun rises in the East, shadows point west. By evening, when the sun is setting in the West, shadows are pointing East. When the sun is low (morning and evening), shadows are long and stretched out. When the sun is high (midday), shadows are short.
The Sun makes the longest shadows at the beginning and end of the day, when the Sun is lowest in the sky.
The Sun makes the shortest shadows at midday, when the Sun is highest in the sky.
Shadows work like a sun dial. The Sun rises in the East. This means that if you are facing North, in the morning the Sun will be on your right and your shadow will be on your left.
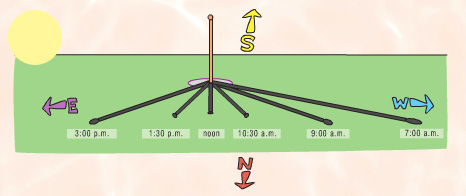
The Sun is in the West in the afternoon. If you are facing North, your shadow will be on your right side, more or less in the 3 PM position.